DBMS Implementation
Note: This article is automatically translated, please turn to the Chinese version for more accurate expression if possible.
Overview
I want to do a database management system DBMS in the elementary school next semester, because I think it is very interesting, so I plan to write it in advance.
some thoughts
First, I want to try the development model of Typescript + Electron. Javascript is almost my favorite programming language at the moment. The syntax is similar to C/C++. It is comfortable to write, and it does not have the uncomfortable indentation of Python; it is also a true cross-platform language, which can be run wherever a browser exists. And with the help of Electron, you can easily implement a cross-platform client, and it is much easier to package up than Python / C++; object-oriented and functional have certain support, especially Typescript brings static type checking to it; the language comes with The single thread/event mechanism makes it inherently asynchronous, which is very convenient to use as a user interface; new technologies also make JS run more efficiently. However, choosing to use JS here also has certain shortcomings. The ecology of JS is mainly in the front end, and some packages may be missing when it is used for this kind of low-level system. In the end, JS was chosen because it was only a course design and would not have high performance and reliability requirements.
Secondly, there are some things about visualization. I especially hope that the working process of the DBMS can be displayed intuitively, especially the SQL parsing piece, which can draw abstract syntax trees and the like, and can also draw table structure, meta-information, etc., I feel a little excited to think of this, which is a big motivation that drove me to do it.
Maybe after the project is completed, it can be more than just a course design. If the logic and visualization are done well, it can be used by teachers for teaching. It can intuitively display SQL analysis, generated relational algebra, optimized content, and there are many things that can be made dynamic Shows, such as multi-granular locks, log-based recovery, of course these are for later.
Finally, completing this project is a gradual process (for example, it supports a small number of expressions first, and then finds that it needs to be added later), but the structure of the article will be messy if it is written in this way, so all articles will be updated at any time during the project.
Design and evaluation
The DBMS is still a fairly large system. The teacher said that when the time comes, we will only allow us to implement a small part of the functions, but I have to do it in advance and plan by myself which parts to implement. In this way, you must list all the modules/functions, divide the dependencies, evaluate the implementation scheme and difficulty, and finally decide the part to be implemented.
The following is a diagram of the structure of a database system:
data structure
Tables in relational databases are stored in two-dimensional arrays. A database contains many tables, and an instance of dbms can contain many databases. At each level here, there will be some metadata that needs to be stored. The initial idea is that metadata is also stored in a table structure, which makes it more convenient to provide users with an editing interface.
File system
The more uncomfortable point is that what I want to implement is a toy model, and there will be no need for a large amount of data, at most, the amount of data at the MB level. At this time, the file system is only used as a persistence solution, not centered on it. . For such a small amount of data can be put into memory completely, file management and buffer management are meaningless. So the implementation of the buffer mechanism is really thankless, so first implement a memory-based database management system, and data access is implemented directly through serialization and deserialization.
Another point is that the reason why the index will be implemented by the b+ tree is that the b+ tree is more compatible with disk operations and requires less reading and writing. Since all the content is in the memory, replacing the b+ tree with other balanced search trees may be the opposite. Faster.
SQL analysis and execution
The interface provided by the DBMS to the user is SQL (DDL + DML), which is also the most complicated part for a small DBMS.SQL grammar belongs to LALR(1) grammar,HereThere are several BNF statements and HTML versions of standard SQL to look at. They are huge. To generate a parser from a grammar, a parser generator is needed. Lex and Yacc can only be used in C/C++. After checking it, I found that there is a ported version of JS called Jison (Bison in Javascript), which can be used without any problems. The complete SQL is too big, and its grammar-guided definition is not something I can complete on my own, so I have to implement a subset of it. Fortunately, I found a copy in an unfinished projectCan be used for the grammar-directed definition of jison, What to do is to streamline or refactor based on it.
reference
In the structural design of the system, reference is made to the redbase database, which contains four main modules: file system, system management, language execution, and index. A physical plan is generated when SQL is executed, and there is no logical plan. Minidb has no file system part. The index has not been implemented yet, and other structures are similar to redbase.
The division of the physical plan mainly refers toSQL Server documentation。
Next step
So far, it has realized the functions of SQL parsing, semantic checking, and execution. It can perform addition, deletion, and modification operations, and it can create, delete, switch databases, and persist data. However, it only implements the operations on the main process. If there are violations, there will still be loopholes. The next step is to visualize the physical plan, adding type checking, data integrity constraints, and then indexing.
Current results:
Project structure
Project structure and development environment construction. There is not much content on the Typescript + Electron project built on the Internet, so it is necessary to describe it separately.
The project adopts the Client-Server structure. The Client provides a user interface and sends user input to the Server through IPC. The Server is responsible for all the remaining work and returns the result to the Client as a string. The Client side implements a rudimentary terminal, using the xterm library.
After the server receives the input, it first determines whether the first character is. Judge the system command, if it is a system command, call the code in the manager module to modify/query system information. If it is a SQL statement, the SQL will be parsed by the parser generated by Jison to get the parse tree. After calling the semantic check function in the query module according to the statement type, it will check the legitimacy of the parse tree and complete the omitted column names in the statement. After the semantic check is over, the query module is responsible for converting SQL statements into execution plans, and all execution plans are in the plan module. Finally, it executes according to the execution plan and converts the output into a string, and returns it to the Client.
Environment setup
Typescript + Electron
With this technology stack, it is more difficult to search for hand-held blogs, and you need to have a certain understanding of the working methods of Electron, Typescript and NPM. Applications can be packaged and released (no production environment), so only the development environment is considered below. The way to use electron on the command line iselectron [filename] , The file is the entry file of electron. NPM configuration fileconfig.json inside scripts The script is run in NPM’s own environment,node_modules The dependencies under the folder will be added to the environment. Typescript is equivalent to adding a compilation step before all normal behaviors. Just specify the directory where the ts file is located and the output directory in the settings.
npm init
npm i typescript -S
npm i electron --save-exact
The version of electron changes quickly, so it is better to store a specific version. TSLint is not needed because it is solo.
Createtsconfig.json , Which makes the compilertsc Read the input from the src folder and set the output to the js folder.
In this way, the running script of NPM istsc && electron ./js/main.js
Terminal
Find a better command-line terminal hterm, influenced byThis articlerecommended.
The main interface of the DBMS is the command line, and xterm is used here.
npm i xterm -S
Simple use is as follows:
import { Terminal } from "xterm";
let term = new Terminal();
term.open(document.getElementById("terminal"));
term.on("key", (key, ev) => {
term.write(key);
});
A useful command line is encapsulated in the back, so I won’t repeat it.
Parser
Parser generator used Jison:
npm i jison -S
The instructions for using Jison to generate a parser are:
jison ./ts/parser/sql.y -o ./ts/parser/parser.js
Since ts is used to compile, this js file will not be placed in the output folder (changing the suffix will cause the compilation to fail), so you have to copy it manually:
copy .\\ts\\parser\\parser.js .\\js\\parser\\parser.js /Y
This is the command under windows.
Webpack
The project is developed using npm, but it is unavoidable to package when it is released, and Webpack will be used. But let’s talk about these boring things when the project is finished.
SQL parsing and execution
Determine the supported SQL subset, and implement the input parsing.
Parser
It is not difficult to write SQL Parser directly by hand. The first word can determine the type of sentence, and the sentence template can be directly applied later, but it is still a little troublesome to parse the expression part. For convenience and clarity, Jison (Yac implemented by js) is used to generate SQL Parser for js.
Mentioned in the first articleSyntax-guided definition for jison, This definition is more than 1,500 lines, it is very troublesome to read, so I wrote a python script to draw a tree diagram of the SQL grammar through Graphviz (due to the recursive definition in the grammar, it is not a tree. Called a dependency graph better).
The above is a vector diagram, you can zoom in as much as you like when you open a new tab page. It’s still tiring to look at the whole picture directly, but thanks to Graphviz’s powerful layout, we can see at a glance what sub-statements are and split them out. The following is the process of checking these statements in turn and condensing them.
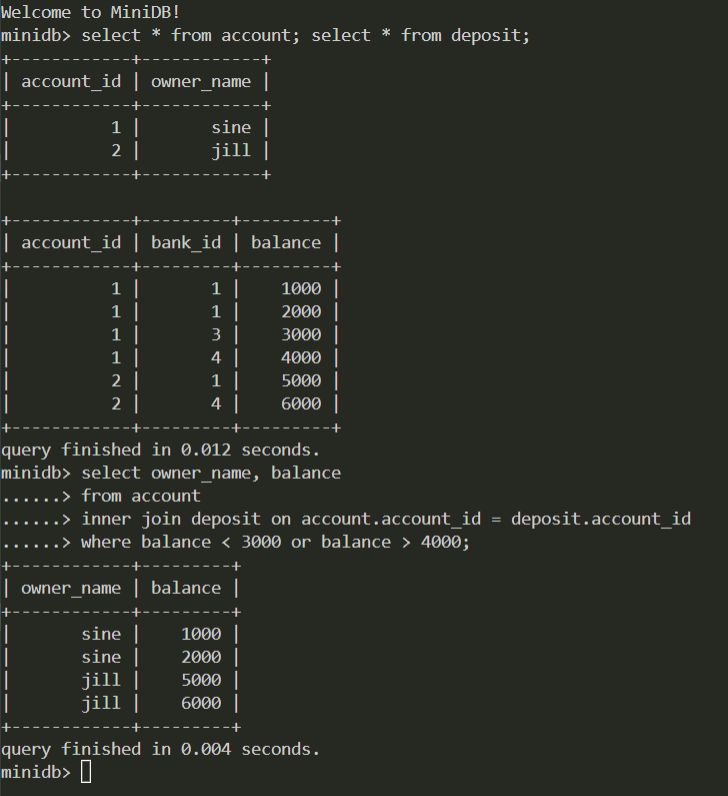
So far, the creation and deletion of tables and the addition, deletion, and modification of data query statements have been implemented:
sql_stmt
: create_table_stmt
| drop_table_stmt
| insert_stmt
| select_stmt
| delete_stmt
| update_stmt
;
In addition to SQL statements, there are also some system commands for database creation, deletion, system management and other operations:
.exit | 退出
.file [filename] | 将文件内容作为输入
.createdb [database name] | 创建数据库
.dropdb [database name] | 删除数据库
.usedb [database name] | 使用数据库
.showdb | 显示所有数据库
.showtb | 显示当前数据库所有表
In order to distinguish it from SQL, all system commands are. begin.
CREATE TABLE statement
First implement a most basic CREATE TABLE statement, and save the integrity constraints.
create_table_stmt
: CREATE TABLE database_table_name LPAR column_defs RPAR
;
database_table_name
: name DOT name
| name
;
name
: LITERAL
;
column_defs
: column_defs COMMA column_def
| column_def
;
column_def
: name type_name
;
type_name
: names
;
The semantic actions can be seen in the code repository, first try the effect of parsing:
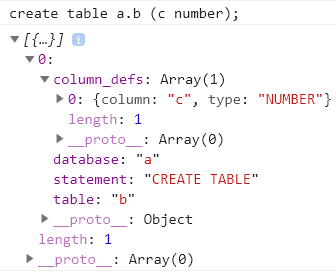
There seems to be no problem.
MiniDB data type
What data types are supported? The maximum length of the string and the precision of the number specified in the standard SQL statement are to facilitate the allocation of storage space. Doing those with js is purely to increase the complexity.
It’s the easiest to use the js original sound data type directly, so let’s do it first.
There are three data types: Number, String, Date.
Although Number is divided into int and float, it is troublesome for js to perform type checking (not the basic data type of js), so it is not supported at first. String is inherently unlimited in length, Date belongs to the object of js, you need to write it when you use itDate('yyyy/mm/dd') 。
INSERT statement
Simply insert a set of data into the table, and there is no type check yet.
insert_stmt
: INSERT INTO database_table_name columns_par insert_values
;
columns_par
:
| LPAR columns RPAR
;
columns
: columns COMMA name
| name
;
insert_values
: VALUES LPAR subvalues RPAR
;
subvalues
: subvalues COMMA expr
| expr
;
expr
: literal_value
| NULL
;
literal_value
: NUMBER
| STRING
;
expression
There are three basic units of expression: literal, NULL and name. The name can be column name or table name. column name or database name. table name. column name. Hereafter the names represent these three.
There are two types of expressions according to the return value type: data type and Boolean type.
Data type expressions connected by comparison operators are called Boolean operators, and Boolean operators are connected by logical connectors or boolean.
expr
: literal_value
| name
| name DOT name
| name DOT name DOT name
| expr EQ expr
| expr NE expr
| expr GT expr
| expr GE expr
| expr LT expr
| expr LE expr
| expr AND expr
| expr OR expr
;
The interpretation of expressions uses function recursion. For numeric types, evaluate directly, while Boolean types recursively calculate the values of the left and right subtrees and then evaluate them.
SELECT statement
The SELECT statement is the most complex part of the entire SQL. A typical SELECT statement looks like this:
SELECT result_columns
FROM table1
(INNER) JOIN table2 ON join_condition
WHERE expression
When creating an execution plan, first perform the table join operation in the FROM clause, then put the large table in the expression of the WHERE clause to filter, and finally use the column that exists in result_columns to get out. No optimization has been considered yet.
select
: SELECT result_columns from where
;
result_columns
: column_list
| STAR
;
column_list
: column_list COMMA name
| name
;
alias
:
| name
| AS name
;
from
: FROM join_clause
;
join_clause
: table_or_subquery
| join_clause join_operator table_or_subquery join_constraint
;
table_or_subquery
: database_table_name alias
;
join_operator
: COMMA
| join_type JOIN
;
join_type
:
| INNER
| CROSS
;
join_constraint
:
| ON expr
;
where
: WHERE expr
|
;
DELETE given UPDATE
The DELETE and UPDATE statements have a relatively simple structure, and the limited statement where has been defined in the previous statement.
delete_stmt
: DELETE FROM database_table_name where
;
update_stmt
: UPDATE database_table_name SET column_expr_list where
;
column_expr_list
: column_expr_list COMMA column_expr
| column_expr
;
column_expr
: name EQ expr
;
Implementation plan
The output of SQL Parser is a syntax tree, and then the program converts the syntax tree into an execution plan and executes it to obtain the table entry output. The execution plan is a good first-level interface. Each plan represents an operation. It mainly provides the get_next() interface to get the next entry. The execution plan provides the program with better modularity and room for optimization. For example, when scanning a table, if an index is not established, only a circular scan plan can be used, and an index scan plan can be used to improve efficiency if there is an index; When the table is connected, it can be realized in three ways: double loop, hash, and merge. The program can choose a better execution plan according to the actual situation.
There are two kinds of plans, logical plan and physical plan. Logical plan is almost a relational algebraic expression, mainly used for optimization, and then converted into physical plan for actual execution. The physical plan mainly refers toSQL Server , Selected some physical plans to be implemented:
compute_scalar
table_filter
hash_join
merge_join
nested_loop_join
aggregate
table_project
table_insert
index_insert
clustered_index_insert
table_delete
index_delete
clustered_index_delete
table_update
index_update
clustered_index_update
table_scan
index_scan
clustered_index_scan
At present, the most basic physical plans without indexes have been implemented, which are enough to support some current SQL statements. When the indexes are implemented in the future, they can be expanded.
Endurance
Persistence refers to saving the data in the memory to the disk so that the previous state can be restored when the program is started next time.
Method to realize
Persistence must rely on the file system provided by the operating system, that is, save data in files. Open the single file of SQLite and look at it, except that the data in the table is all garbled, indicating that it is saved in its own prescribed format, that is, at the binary level. Although NodeJS also provides an interface to do this, there is no need to design a sophisticated storage format, because after all, it is just for fun. The easiest way is to directly serialize the database object and save it in a file in the form of a string. Just parse the file in JSON format when reading it.
Object persistence
After serializing an object, the methods held by the object will be lost, and will not be the original object when it is restored. In order to solve this problem, I had to manually write a method to read data from json for each object. Storing objects and data together will cause inconvenience to persistence. If the two are separated, there is no problem. Objects only store data, and other operations are performed by independent functions. This may be the direction to be reconstructed later.